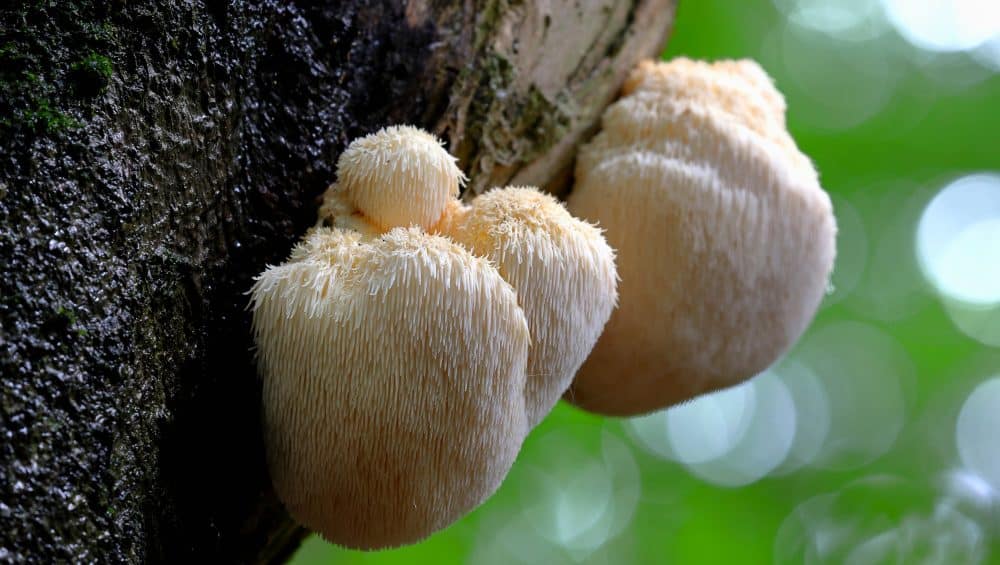
Introduction To Lion’s Mane
Lion’s mane mushroom, also known as Hericium erinaceus, is an edible mushroom native to North America, Europe, and Asia. It is known for its unique appearance, with long, white, cascading tendrils that resemble a lion’s mane. In recent years, lion’s mane mushrooms have gained attention for their potential cognitive-enhancing and mood-boosting properties.
Studies have suggested that compounds found in lion’s mane, such as hericystin and erinacine, may promote the growth and repair of nerve cells in the brain, leading to improved cognitive function. In addition, lion’s mane may also contain anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compounds, which may contribute to its potential mood-boosting properties. However, more research is needed to fully understand how lion’s mane may improve cognitive function and mood and establish its safety and efficacy.

How Lion’s Mane Boosts Mood
Inflammation is known to play a role in the development of mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety. So the anti-inflammatory properties of lion’s mane may help reduce symptoms of these conditions. In addition, lion’s mane’s antioxidant properties may also help protect the brain from damage caused by free radicals, which can contribute to the development of mood disorders.
Another potential mechanism by which lion’s mane may improve mood is stimulating nerve growth factor (NGF) production. NGF is a protein that plays a critical role in the development and survival of nerve cells, particularly in the hippocampus, a brain region involved in mood regulation. Lion’s mane can stimulate the production of NGF in the brain, which promotes the growth and repair of nerve cells in the hippocampus and potentially improves mood.
It’s also worth mentioning that lion’s mane mushroom also contains compounds that may directly affect mood-related neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and GABA. Studies have suggested that these compounds may modulate the activity of these neurotransmitters. These could help improve mood.

How Lion’s Mane Boosts Memory
The mechanisms by which lion’s mane mushrooms may improve memory still need to be fully understood. However, some research suggests that compounds found in lion’s mane may promote the growth and repair of nerve cells in the brain, leading to improved cognitive function and memory. In addition, these compounds also have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, which could protect the brain from damage caused by free radicals and inflammation, which can contribute to cognitive decline and memory loss.
Moreover, lion’s mane may also have a direct effect on memory-related neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that plays a critical role in learning, memory, and attention. Studies have suggested that compounds found in lion’s mane may modulate the activity of acetylcholine, which could help improve memory.

The Science Behind Lion’s Mane
Numerous scientific studies have been conducted on lion’s mane mushrooms and their potential health benefits. Some studies have found that compounds found in lion’s mane may promote the growth and repair of nerve cells in the brain, leading to improved cognitive function and memory. For example, a study published in the Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine found that supplementing with lion’s mane mushroom extract for 16 weeks improved cognitive function and memory in older adults with mild cognitive impairment.
Other studies have found that lion’s mane may have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. This may help protect the brain from damage caused by free radicals and inflammation, which can contribute to cognitive decline and memory loss. A study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food found that lion’s mane mushroom extract has significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in mice.

The Benefits Of Lion’s Mane
Lion’s mane mushroom has been shown to have a number of potential health benefits. Some of the most well-studied potential benefits are listed below.
- Improving cognitive function and memory: Some studies have found that compounds found in lion’s mane may promote the growth and repair of nerve cells in the brain, leading to improved cognitive function and memory.
- Boosting mood: Lion’s mane may contain anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compounds, contributing to its potential mood-boosting properties.
- Supporting a healthy immune system: Lion’s mane mushrooms are known to have compounds that may boost the immune system, which can help fight off infections and illnesses.
- Supporting cardiovascular health: Lion’s mane mushrooms may have compounds that can help reduce inflammation and lower cholesterol levels, which can benefit cardiovascular health.
- Supporting healthy digestion: Lion’s mane mushrooms may have compounds that can help promote healthy digestion and regulate gut bacteria.

How To Use Lion’s Mane
Here are several ways to consume lion’s mane mushrooms.
Dried mushroom: Dried lion’s mane mushrooms can be found in many health food stores and can be rehydrated and added to soups, stews, and stir-fries.
Extract: Lion’s mane mushroom extract is also widely available in supplement form and can be found in capsules, tablets, and powders.
Tea: Lion’s mane mushrooms can also be consumed as tea by brewing dried or powdered mushrooms in hot water.
Tincture: Lion’s mane mushroom tincture is an alcohol-based extract taken by dropping the extract under the tongue or adding it to a drink.
Culinary uses: Lion’s mane mushrooms can also be used as a culinary ingredient. They are often sautéed, grilled, or fried and can be added to dishes such as omelets, pasta, and risotto.
It’s important to note that the recommended dosage of lion’s mane mushroom can vary depending on its consumed form. It is recommended to consume two to three grams per day for dried mushrooms. For extract, dosages of 500-3000 mg per day are commonly recommended, and for tinctures, a standard dose is 30-60 drops, taken two to three times per day. However, it’s worth mentioning that there has yet to be a standardized dosage, and more research is needed to determine the optimal dosage for lion’s mane mushrooms.
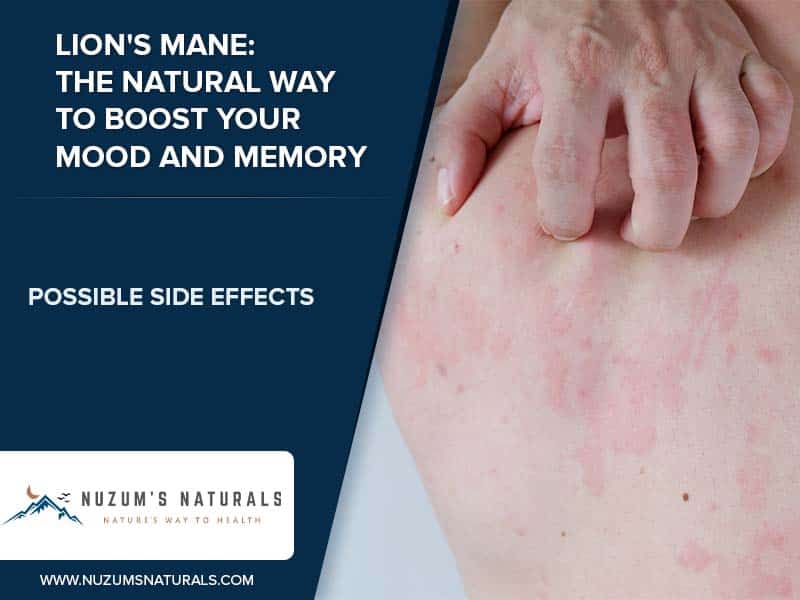
Possible Side Effects
Lion’s mane mushrooms are generally safe for most people when consumed in moderate amounts. However, as with any supplement, some people can experience side effects. For example, some people may be allergic to lion’s mane mushrooms and may experience hives, itching, and difficulty breathing. Others may experience stomach upset, nausea, or diarrhea when consuming lion’s mane mushrooms.
Lion’s mane mushrooms may interact with certain medications, particularly blood thinners. Therefore, you must consult with a healthcare professional before taking lion’s mane mushrooms if you are taking any medications. There has also not been much research on lion’s mane mushrooms’ safety during pregnancy and breastfeeding, so it may be safer to avoid using it during these times. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking lion’s mane mushroom supplements for extended periods, especially if you have any pre-existing medical conditions or are taking any medications.
It’s also worth mentioning that not all lion’s mane mushroom supplements are created equal. For example, some supplements may contain fillers or other ingredients, and the quality of the mushrooms used in the supplement can also vary. Therefore, it’s important to purchase supplements from reputable sources and to check the label for any potential allergens or contaminants.

How To Choose A Quality Product
When purchasing a lion’s mane mushroom supplement, there are a few things to consider to ensure that you are getting a high-quality product.
- Look for third-party testing: One of the best ways to ensure that a supplement is high-quality is to look for third-party testing. This means that an independent lab has tested the supplement and has verified that it contains the ingredients listed on the label and is free of contaminants.
- Check the label: Be sure to check the label for any potential allergens or contaminants. Also, look for information about the form of the mushroom supplement, whether it is in the form of extract, capsules, powder, or tincture.
- Look for organic or wild-harvested mushrooms: Lion’s mane mushrooms that are organically or wild-harvested are less likely to be contaminated with pesticides or heavy metals.
- Quality of the mushrooms: The quality of the mushrooms can also vary. A high-quality supplement will use mushrooms grown in a proper environment, with a balanced diet, and without any chemicals or irradiation.
- Check the source: Try to purchase from a reputable source, whether it’s a store or a website. Also, check for certifications and awards that the company or product has. These certifications and awards can be good indicators of quality.
- Consult with a healthcare professional: Before taking any supplement, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional. They can help you determine if a particular supplement is safe and appropriate for you, and they can also help you identify any potential interactions with medications you may be taking.

Combining Lion’s Mane With Other Nootropics
There are several nootropics that have been suggested to enhance the effects of lion’s mane mushrooms. Here are some of the most commonly suggested nootropics to combine with lion’s mane.
Acetyl-L-carnitine (ALCAR): ALCAR is an amino acid that can help improve memory and cognitive function. It has been suggested that ALCAR may enhance the effects of lion’s mane by promoting the growth and repair of nerve cells in the brain.
Phosphatidylserine (PS): PS is a phospholipid found in the brain and helps improve cognitive function and memory. PS may enhance the effects of lion’s mane by improving the function of nerve cells in the brain.
Bacopa monnieri: Bacopa monnieri is a plant that has been traditionally used to improve cognitive function and memory. It has been suggested that Bacopa monnieri may enhance the effects of lion’s mane by promoting the brain’s growth and repair of nerve cells.
Ginkgo biloba: Ginkgo biloba is an herb that has been traditionally used to improve cognitive function and memory. It has been suggested that Ginkgo biloba may enhance the effects of lion’s mane by improving blood flow to the brain.

It’s worth noting that there is limited research on the effectiveness of combining lion’s mane mushrooms with other nootropics. It’s always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before combining any supplement, especially if you are taking any medications. Additionally, it’s essential to be aware that these combinations may increase the risk of side effects and interactions.
So it’s important to be cautious. Monitor any changes in your body or mind when taking these combinations. As always, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before adding any new supplement to your diet, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, have a medical condition, or are taking any medications.

